General
Sound card based PSK31 Phase Shift Keying at a Baudrate of 31Bd has become a very popular mode for digital communication in Amateur Radio these days. Unlike using external hardware devices as described in the topic on The Multimode Facility the PC's on board sound card is tasked for generating the sophisticated tones which contain the coded digital modulation. This is by all means the cheapest access to digital communication. Based on the fundamental work of Peter Martinez, G3PLX, Moe Wheatley, AE4JY, has created a DLL Dynamic Link Library for WINDOWS applications ( http://www.moetronix.com/ae4jy ). Thanks for a great job, Moe!
We have fully embedded this DLL in TurboLog 4. Thus, we can offer PSK31 operation along with all the other features already existing in TurboLog 4. Of course the QSO data can automatically be logged under the various logging modes as available in TurboLog 4. The DLL offers the following features:
•Multiple sound card support.
•Allows multiple independent receiver channels(1 to 50) (*).
•Ability to enable and disable receive channels while running (*).
•Threshold adjustable noise activated squelch control.
•PSK31 Signal strength/quality value available for squelch and display.
•Soft decision Viterbi decoder for QPSK mode
•Symbol Vector tuning data for phase type display.
•Frequency Spectrum data available for Display 0 to 4000 Hz with 3.9Hz resolution.
•Log or 4th root frequency spectrum data formats.
•Raw soundcard data mode.
•S/N Signal to Noise Ratio qualified IMD Intermodulation Distortion measurement data.
•Soundcard clock error measuring and compensating capability.
•Includes Serial COM port RTS and/or DTR PTT control.
•CW ID capability with multiple speed selections.
•32000 character transmit buffer.
•Full duplex Tx and RX mode can be invoked.
•A fast AFC Automatic Frequency Control mode can be used to track doppler shifting BPSK Binary Phase Shift Keying signals up to +/-20Hz/Sec.
•Ability to read and write to RIFF PCM Pulse Code Modulation wave files for decoding or storing raw audio (*).
•Double/Quad Speed BPSK and QPSK Quadrature Phase Shift Keying(PSK63 and PSK125).
•Split operation in audio base band under mouse control
(*) denotes features which are currently not activated.
Please note:
While the sound card is in use for digital operations no Packet related hear alerts can be generated. The user does not need to care for turning the alerts on or off. The alerts are automatically interrupted as long as the sound card based operation is going on.
Implementation
The sound card based PSK31 facility is implemented within the framework of the Multimode Facility. Thus you should familiarize yourself with the basic principles of operating the Multimode Facility. Basically, the PSK31.DLL is just treated as another "device". Thus, the setup for the PSK31.DLL is an integral part of the MultiMode setup. Consequently, you only need to move into the Configuration menu, select Devices and finally sub item Multimode Controller. You will have to select PSK31_Sound from the Devices' drop down box and load the default Command/Script and Device Buttons. They are ready to use and should be fully sufficient for the immediate start of PSK31 operation. If you consider PTT control for your transceiver you finally need to select a unique Comport for yielding the appropriate output signals and the correct timing.
After you have correctly setup the PSK31 device you can start MultiMode operation from anywhere in TurboLog 4 by pressing Ctrl+D.
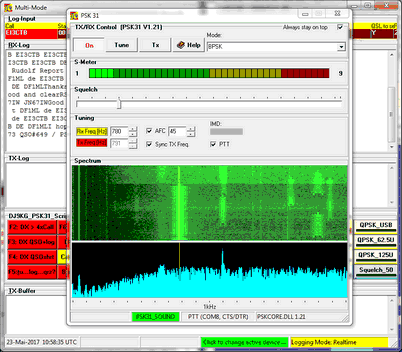
This will open two windows as shown below. ( For the aim of rendering in one screen shot both windows are shown in an overlay position ) :
Since the underlying MultiMode Window is described in greater details in a separate paragraph we would like to draw the user's attention to this topic an just make reference to its basic properties here. However, please note the dedicated sets of buttons in the lower part of the MultiMode Window. They were created for this particular kind of PSK31 operation. While the left group box contains scripts or macros which can be triggered off for transmission by clicking the appropriate button, the group box to the right contains remote control buttons for the PSK31Form. This means that all important controls of the PSK31 facility can either be operated by means of the button array or directly from the control elements of the PSK31Form. We recommend, however, to operate from the button array in order to maintain synchronization of button states and controls on the PSK31Form.
The PSK31Form contains controls and in particularly displays which are specific for the sound card based PSK31 operation. These are the controls for the BPSK operations:
Always stay on top:
With this check box being ticked the PSK31 frame will always stay on top of all other open windows.
RX Indicator:
The yellow line indicates the receive frequency. It can be moved by left mouse key click over the waterfall display to any position within the audio band on display.
TX Indicator:
A red line indicates the transmit frequency. It will be covered by the yellow line if Sync TX Freq is checked and transmit frequency equals receive frequency. Otherwise the red line can be moved by right mouse key click over the waterfall display in order to facilitate split operation within the audio base band.
ON:
Pressing this toggle switch button will turn the PSK31 facility on. The equivalent remote button is BPSK31 ON. Start-up mode of operation of the facility is receive.
Tune:
Pressing this toggle switch button will turn the facility into transmit mode. The equivalent remote button is Tune. An unmodulated tone is generated which can be used for testing and tuning the transceiver.
Tx:
Pressing this toggle switch button will start transmitting the two narrow spaced tones which characterize the PSK31 transmission mode. The equivalent remote button is RX/TX Toggle. The two tone signal remains unmodulated as long as no data is keyed from script buttons or directly from the keyboard into the TX buffer of the MultiMode window.
Mode:
This drop down box allows you to select various other BPSK modes which are all derivatives of PSK31. All modes are mapped on buttons. For the time being the following modes are available:
BPSK31
QPSK USB
QPSK LSB
BPSK62.5
QPSK62.5 USB
QPSK62.5 LSB
BPSK125
QPSK125 USB
QPSK125 LSB
S-Meter:
This display will show the relative signal strength of the received signal.
Squelch:
This slider allows you to adjust the threshold for good signal detection and print.The squelch level may vary in the range 0 ... 99.
RxFreq:
This thumb wheel displays the numerical value of the audio receive frequency. Its label is on yellow background color in order to indicate receive mode. Frequency should be changed by mouse action.
Please note:
If the AFC is activated the frequency may move a little bit in order to follow a carrier or because of random noise on the band. Ticking/unticking the SyncTxFreq check box may be necessary from time to time but not be performed while in QSO.
TxFreq:
This thumb wheel displays the numerical value of the audio transmit frequency. Its label is on red background color in order to indicate transmit mode. Frequency should be changed by mouse action.
AFC:
The automatic frequency control will tune receive frequency exactly on to the PSK carrier, if check box is ticked. The capture range can be adjusted by means of the thumb wheel button. A capture range of about 30 Hz is sufficient.
SyncTxFreq:
This control will synchronize receive and transmit frequency, if ticked. Uncheck if you want to start split operation.
IMD:
The InterModulation Distortion measurement facility measures 3rd order intermodulation products which will be the result of overloading the input of the soundcard. In case of overloading the input resulting IMD-products will be displayed in dB relative to the level of the PSK31 main signal. This is extremely helpful for setting up a soundcard based PSK31 system.
PTT:
Checking this box will enable switching between RX and Tx via the output of a selected Comport instead of using the transceiver's voice control ( VOX Voice Operated Transmitting ). PTT Push to Talk switching should be preferred in order to prevent your rig from being triggered unintentionally by other output signals from the sound card. A unique comport has to be selected in the Devices Setup for PTT purposes. If there are no more comports on your PC you will need an USB to Serial Port converter. The switching pin of the comport's output can be adjusted in the Turbolog.ini file, section [PSK31Settings], parameter PTTMode. The following options are provided:
0 = No serial port PTT.
1 = Use RTS only.
2 = Use DTR only.
3 = Use RTS and DTR (default mode).
Serial port and PTTMode information is displayed in the Status bar, Panel 3 from left. By default the PTT switching signal is output on the DTR and RTS pins of a standard DB-connector. The signal is polarized as to pull down a switching transistor.
Spectrum waterfall display:
This fancy display allows to monitor spectral power density versus time. This is ideal for finding and tuning to PSK31 signals and to monitor the signal to noise ratio during reception and transmission.
Power spectrum:
The frequency range on display is about 2000Hz. The power spectrum display is computed by means of a 2048 points FFT Fast Fourier Transformation. Since the sample rate of the audio signal is 8000Hz the resulting frequency resolution is 3.906Hz per bin. While the frequency axis is divided linearly the power axis is displayed at logarithmic units. An unmodulated PSK31 signal consists of two audio carriers separated by 31.25 Hz.
Status bar:
The status bar consists of 4 panels. The left panel [ logical 0 ] is used by the PSK31.DLL for the output of messages, such as:
Transmit
Receive
ON
OFF
Input Overload, etc.
Change active device
The second left panel [ logical 1 ] shows the device's name ( PSK31_Sound ) on green background color. This panel comes up if the PSK31 facility has been turned on.
Panel 3 from left [ logical 2 ] contains PTT comport status information.
Finally, panel 4 [ logical 3 ] may be accessed by the user for display of customized messages defined under the Device Buttons.
The rightmost panel allows you to change the active multimode device on the flight (see itemization below, 10th item ).
Getting started
In order to start PSK31(=BPSK31) operation you should follow this sequence:
•Get yourself a suitable sound card interface. This piece of hardware should be equipped with 2 audio transformers for both sound channels ( Input & Output ) of the sound card. Furthermore, there should be at least one opto-coupler for the PTT-signal generated by the serial Comport.
•Press Ctrl+S and move into the Configuration Menu and make the necessary adjustments under sub item Devices ( e.g. select PSK31_Sound as device, unique ComPort for PTT-operation, etc ).
•Press Ctrl+D from anywhere in the program in order to activate the MultiMode facility. If you had selected PSK sound card operation the PSK31Form will pop up along with the MultiMode window.
•Set your transceiver to the lower edge of the PSK sub band, e.g. 14070.00KHz and change into USB mode.
•Press the yellow BPSK31 ON button, this will start the receive mode.
•Press the Direct Send button, this will enable direct transmitting any macros from Command/Script Buttons such as, e.g. DX >4xCall.
•Press the RX/TX button in order to toggle between receive and transmit operation.
•After you have monitored the band and found a clear spot you could now press the green F6: CQ call...k button, for example, which starts a CQ call. Likewise you could have pressed the F6 key. Both actions yield equivalent results since the CommandButton is equipped with a short cut key by default. Provided your cabling is correct your transceiver is automatically turned on ... and off after the message has been transmitted, respectively.
•Transferring QSO data from the MultiMode's RX window into the log input line and logging itself is described in greater details in the paragraph on The MultiMode Facility.
•Please note:
If you run more than one external/internal MultiMode device you will not like to adjust the required distinct Comport parameters attached to the device while you switch from one to the other. In order to ease this trouble you can edit the device Settings ( see paragraph on: Device Configuration ) by applying/modifying an entry line, for example:
COMPORT COM1,9600,8,N,1
This entry will fix the inputs of the Comport Configuration and overrule in case of discrepancies!!
•Fastest procedure for switching between MultiMode devices: Just left key click once on the rightmost panel of the status bar which is labeled:  . Select the device you want to run as next from the drop down box which comes up. If you want to leave without making any changes you must click the Cancel button. Clicking the Accept button will close the Multimode window and reopen it with the user defined features of the new device. This device will also become the new default to come up with the Ctrl+D command when pressed next time.
. Select the device you want to run as next from the drop down box which comes up. If you want to leave without making any changes you must click the Cancel button. Clicking the Accept button will close the Multimode window and reopen it with the user defined features of the new device. This device will also become the new default to come up with the Ctrl+D command when pressed next time.
•Furthermore, of course you can still go the slow way via the Configuration menu. If you want to do this: Close MultiMode window, if open. Press Ctrl+S, select Log Setup, sub item Devices/MultiMode Controller, select Device, press Apply and leave. Press Ctrl+D in order to return into MultiMode operation with the new device.
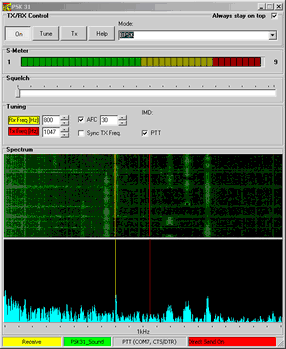
Going to Split Operation:
•Uncheck SyncTxFreq.
•Tune to the signal you want to receive by left mouse key click over the waterfall display. The red transmit frequency line now becomes visible.
•Move to the frequency you want to transmit on by right mouse key click over the waterfall display.
•An example is shown on the screen shot below:
.
The screen shot example shows the receive frequency ( yellow line ) tuned to a PSK31 signal on 800Hz while the transmit frequency ( red line ) is "up" by 247Hz.
ACTIVE COMMANDS:
KEYS:
| Accept | Button on change active device frame, saves selection and closes box |
| Cancel | Button on change active device frame, closes box without any changes |
| Ctrl+A | Selects all text in frame. |
| Ctrl+Delete | Deletes all selected text. |
| Ctrl+D | Opens the MultMode window. |
| Ctrl+S | Opens the Configuration menu for MultiMode setup. |
| Ctrl+Enter | Enters text from TX-Buffer into TX-Log. |
| Enter | Logs QSO. |
| Cursor+Down | ...from call field: Triggers DXCC analysis; sets Start time. |
| Shift+Cursor | Pushes text from TX Log into logging field. |
| Shift+CursorRight | Pushes text from TX Log into logging field. |
| Shift | Pushes text from TX Log into logging field. |
| Shift | Set Start time for logging. |
| Ctrl+X | Cut selected text. |
| Ctrl+C | Copy selected text. |
| Alt+ ... | User definable short cuts ... . |
| F1...F12 keys | User definable short cuts assigned to buttons. |
| Alt +F... keys | User definable short cuts assigned to buttons. |
| Shift+F... keys | User definable short cuts assigned to buttons. |
| Ctrl+F... keys | User definable short cuts assigned to buttons. |
CLICKABLES and HOTSPOTS:
| Left mouse key click over the waterfall display | set receive frequency. |
| Right mouse key click over the waterfall display | set transmit frequency for split operation. |
| Tool tips | popping up on mouse over. |
This topic was last edited on Thursday, 12-Dec-2024, at 13:30